|
|
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
|
|
|
|
<h1 align="center">Quick Sort Source</h1>
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[What It Is](#what-it-is)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## What It Is
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Like **[MergeSort](https://github.com/Dentrax/Data-Structures-with-Go/tree/master/merge-sort)**, `QuickSort` is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. There are many different versions of quickSort that pick pivot in different ways.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Always pick first element as pivot.
|
|
|
|
|
* Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
|
|
|
|
|
* Pick a random element as pivot.
|
|
|
|
|
* Pick median as pivot.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The key process in quickSort is `partition()`. Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x. All this should be done in linear time.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QuickSort(arr[], start, end)
|
|
|
|
|
--------------------------
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Partition Algorithm**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
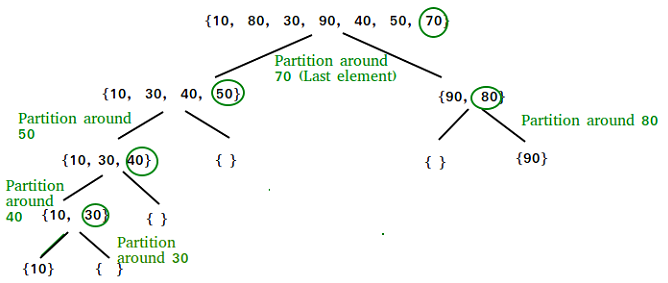
There can be many ways to do partition, following pseudo code adopts the method given in CLRS book. The logic is simple, we start from the leftmost element and keep track of index of smaller (or equal to) elements as i. While traversing, if we find a smaller element, we swap current element with arr[i]. Otherwise we ignore current element.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
> * Input: {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5}
|
|
|
|
|
> * Output: Sorted array is `1 5 7 8 9 10`
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Algorithm Complexity**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Complexity | Notation |
|
|
|
|
|
| ----------------- |:------------:|
|
|
|
|
|
| `Time Complexity` | `O(n log n)` |
|
|
|
|
|
| `Auxiliary Space` | `O(n)` |
|